Differences between Lubricated and Non-Lubricated Plug Valves
On this page
Plug valves are essential components in fluid control systems due to their simple structure, ease of operation, and excellent sealing performance. They are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical, mining, and others. Depending on the lubrication method, plug valves can be classified into lubricated and non-lubricated types. This article will explore the structure, working principles, advantages and disadvantages, and specific applications of these two types of plug valves, aiming to assist engineers and designers in selecting the most suitable valve type for practical work.
Lubricated Plug Valves
Lubricated plug valves stand out among many valves due to their superior sealing ability and fluid control capabilities. The core component is a hollow plug, and an internal lubrication system effectively reduces friction and extends service life. We will next discuss the structure and working principle of lubricated plug valves and analyze their practical applications in high-demand environments.

1. Structure and Working Principle
The key component of a lubricated plug valve is the plug, which contains a hollow chamber. The bottom of the plug connects to a lubrication chamber, while the top has a sealant injection port to ensure a continuous supply of lubricant. The lubricant flows into the cavity through a small check valve located below the injection fitting, preventing backflow.
2. Lubrication Mechanism
The lubricant enters the lubricating grooves on the surface of the plug through radial holes from the central cavity, providing constant lubrication. The design of the lubrication grooves can vary to ensure even distribution of lubricant across the plug surface. This not only reduces the operating force required when opening or closing the valve but also ensures smooth movement of the plug within the valve body, preventing jamming due to friction.
3. Key Features
Corrosion Resistance: The lubricant effectively prevents corrosion of the plug, extending the valve's lifespan. Choosing a suitable lubricant is especially important for high-corrosion media.
Sealing Ability: High-quality sealants maintain good sealing performance, reducing the risk of leaks. In high-pressure environments, effective sealing is essential for safe and efficient system operation.
Adaptability: Lubricated plug valves can be made from various materials (such as stainless steel, carbon steel, alloys), making them suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure working environments.
Reliability: These valves typically experience less wear and can withstand frequent opening and closing operations, making them suitable for long-term use.
4. Application Areas
Lubricated plug valves are widely used in the following fields.
Oil and Gas Industry: Used for high differential pressure shutoff, venting, receiving and sending ball barrels, inlet manifolds, and mud shutoff, their excellent leak prevention and flow control performance make them a crucial choice in this sector.
Mining Industry: Employed in applications such as slurry transportation. Lubricated plug valves offer good wear resistance and corrosion resistance in slurry environments, ensuring continuity and stability in production lines.
Chemical Industry: In highly corrosive environments, lubricated plug valves ensure the safety of fluids and the reliability of systems, especially when handling strong acids and bases.
Food and Pharmaceutical Industry: These valves ensure the purity and safety of fluids in sectors with high hygiene standards.
Non-Lubricated Plug Valves
Non-lubricated plug valves differ in design from lubricated plug valves, utilizing non-metallic elastic sleeves or liners to effectively reduce friction between the plug and valve body. This structure allows for lower maintenance needs, making them suitable for general fluid control environments. Next, we will explore the working principles, structural characteristics, and applications of non-lubricated plug valves in specific industries.
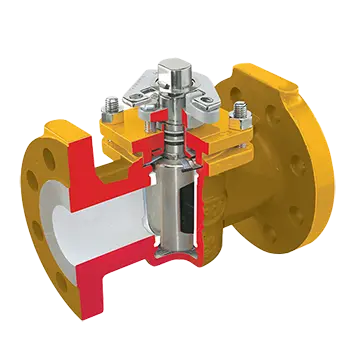
1. Structure and Working Principle
Non-lubricated plug valves use non-metallic elastic sleeves or liners, reducing friction between the plug and valve body. The polished tapered plug acts as a wedge, compressing the sleeve against the valve body to ensure effective sealing of the fluid. Compared to lubricated plug valves, non-lubricated plug valves have a simpler structure and lower maintenance frequency.
2. Key Features
Low Maintenance Needs: These valves typically require less maintenance due to the use of non-metallic materials, making them suitable for long-term operation. Their design reduces wear on mechanical parts, extending service life.
Sealing Ability: Non-lubricated plug valves also provide airtight closure, ensuring no fluid leaks. Their 360-degree fully enclosed sealing design offers enhanced sealing performance.
Cost-Effectiveness: With lower manufacturing costs, they are ideal for budget-conscious projects. The use of non-lubricated materials not only reduces costs but also improves overall valve performance.
Flexibility: The design of non-lubricated plug valves allows for material selection based on the properties of the media, enhancing adaptability.
3. Application Areas
Non-lubricated plug valves, also known as soft-sealed plug valves, are typically used in the following environments.
Corrosive Media: Suitable for fluid control involving corrosive, highly toxic, and hazardous substances. The advantage of the soft seal design is its ability to effectively prevent fluid leaks, ensuring safety.
Strict Leak-Free Environments: These valves perform exceptionally well in industrial environments where any leaks must be avoided, such as in petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Non-High Temperature Conditions: They are suitable for applications at lower temperatures, ensuring stable valve performance. Typically used in general fluid control applications rather than extreme temperature environments.
Water Treatment and Supply Systems: Widely used in drinking water networks and wastewater treatment systems to ensure safe fluid flow.
Conclusion
Lubricated and non-lubricated plug valves each have their unique features. The former is suitable for high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive environments, while the latter, due to its simplicity and low maintenance, is widely used in various general conditions. When selecting a plug valve, users should carefully consider the system's operating environment, fluid properties, budget constraints, and maintenance requirements. A comprehensive assessment of these factors will help choose the appropriate type of plug valve, enhancing the overall performance and safety of fluid control systems, ensuring efficient and stable industrial production.

