Optimizing Gate Valve Performance: Common Issues and Repairs
Gate valves are fundamental components in various industrial processes, employed for regulating the flow of fluids. However, like any mechanical device, gate valves are susceptible to malfunction due to factors such as prolonged use, environmental conditions, and the nature of the fluids they handle. In this article, we will explore the common issues encountered with gate valves and the corresponding repair methods to ensure their optimal performance and longevity.
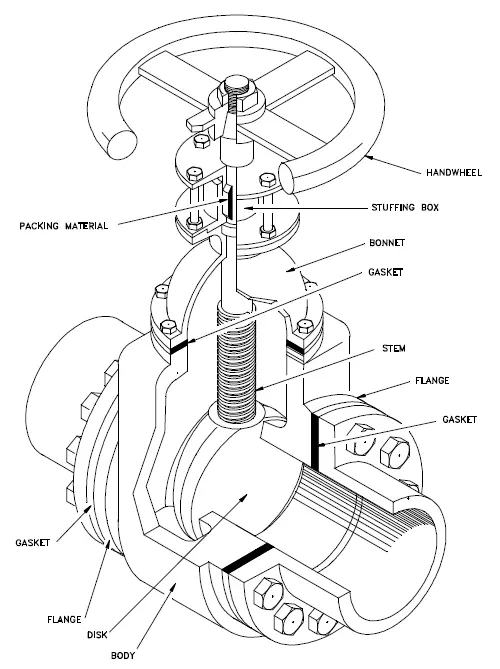
Common Issues with Gate Valves
Gate valves play a crucial role in controlling fluid flow across diverse industrial settings. However, they are susceptible to various common issues that can compromise their performance and disrupt operations. Some of the prevalent issues encountered with gate valves include:
Repair Methods for Common Gate Valve Issues
Repair methods for common gate valve issues typically involve addressing specific problems encountered. Here are the repair methods for some common issues:
In summary, gate valves are essential in industrial processes but prone to issues like leakage, corrosion, and abrasion. To maintain their efficiency and longevity, timely repair methods such as addressing external and internal leakage, and tackling corrosion and abrasion, are crucial. By promptly addressing these common issues, we can ensure uninterrupted operation and reliable fluid flow control in industrial applications.

Common Issues with Gate Valves
Gate valves play a crucial role in controlling fluid flow across diverse industrial settings. However, they are susceptible to various common issues that can compromise their performance and disrupt operations. Some of the prevalent issues encountered with gate valves include:
1. Leakage Problems
External Leakage: External leakage is often observed at the packing gland and flange connections. Causes may include worn-out or inadequate packing material, stem wear, loose packing gland nuts, damaged gaskets, poor flange surface machining, improper bolt tightening, or inadequate pipeline configuration.
Internal Leakage: This occurs when the valve fails to achieve a complete seal due to damaged sealing surfaces or improper seating of sealing rings.
2. Corrosion Challenges
Corrosion is a prevalent issue affecting components such as the valve body, bonnet, stem, and flange sealing surfaces. It is primarily induced by chemical reactions with the medium being transported, alongside ion release from packing and gaskets.
3. Abrasion Concerns
Abrasion refers to localized surface damage, typically seen on gate and seat surfaces, occurring under certain contact pressure conditions.
External Leakage: External leakage is often observed at the packing gland and flange connections. Causes may include worn-out or inadequate packing material, stem wear, loose packing gland nuts, damaged gaskets, poor flange surface machining, improper bolt tightening, or inadequate pipeline configuration.
Internal Leakage: This occurs when the valve fails to achieve a complete seal due to damaged sealing surfaces or improper seating of sealing rings.
2. Corrosion Challenges
Corrosion is a prevalent issue affecting components such as the valve body, bonnet, stem, and flange sealing surfaces. It is primarily induced by chemical reactions with the medium being transported, alongside ion release from packing and gaskets.
3. Abrasion Concerns
Abrasion refers to localized surface damage, typically seen on gate and seat surfaces, occurring under certain contact pressure conditions.
Repair Methods for Common Gate Valve Issues
Repair methods for common gate valve issues typically involve addressing specific problems encountered. Here are the repair methods for some common issues:
1. External Leakage Repair
Adequate packing compression and ensuring symmetrical tightening of packing gland bolts to prevent gland misalignment.
Inspection of flange connections for damaged gaskets, with timely replacement and attention to material selection and machining quality.
Proper tightening of flange bolts and ensuring rational pipeline configuration to prevent external leakage.
2. Internal Leakage Repair
Rectification of damaged sealing surfaces and ensuring proper seating of sealing rings.
Replacement of sealing rings or grinding repair for severe damage to achieve a tight seal.
3. Addressing Corrosion and Abrasion
Adopting appropriate measures according to specific conditions, such as removal of corrosion products, repair of stem surfaces, and replacement of packing.
Adequate packing compression and ensuring symmetrical tightening of packing gland bolts to prevent gland misalignment.
Inspection of flange connections for damaged gaskets, with timely replacement and attention to material selection and machining quality.
Proper tightening of flange bolts and ensuring rational pipeline configuration to prevent external leakage.
2. Internal Leakage Repair
Rectification of damaged sealing surfaces and ensuring proper seating of sealing rings.
Replacement of sealing rings or grinding repair for severe damage to achieve a tight seal.
3. Addressing Corrosion and Abrasion
Adopting appropriate measures according to specific conditions, such as removal of corrosion products, repair of stem surfaces, and replacement of packing.
In summary, gate valves are essential in industrial processes but prone to issues like leakage, corrosion, and abrasion. To maintain their efficiency and longevity, timely repair methods such as addressing external and internal leakage, and tackling corrosion and abrasion, are crucial. By promptly addressing these common issues, we can ensure uninterrupted operation and reliable fluid flow control in industrial applications.

