Understanding Forged Steel Gate Valves
Forged steel gate valves are crucial components in industrial fluid control systems, renowned for their robust construction and reliable performance. Engineered from forged materials such as A105, F11, F5, 304, 304L, 316, and 316L, these valves play a pivotal role in regulating fluid flow across various industries. This introduction provides an overview of the features, advantages, and applications of forged steel gate valves, highlighting their importance in ensuring efficient and dependable fluid control in industrial settings.
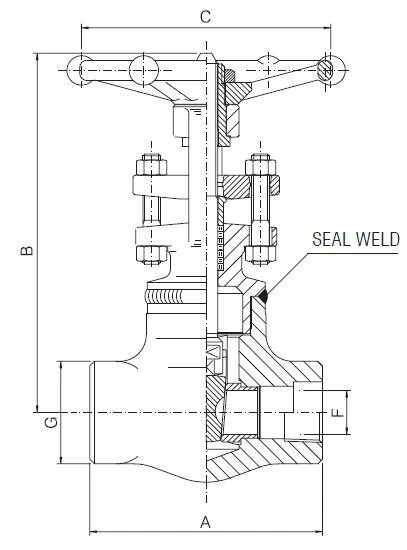
Features of Forged Steel Gate Valve
Forged steel gate valves are distinguished by several key features that contribute to their reliability and effectiveness in industrial fluid control systems:
- Structural Design: Forged steel gate valves feature a reduced bore design, ensuring resilience to high pressures and temperatures. Despite slightly reduced flow compared to cast steel gate valves, they offer superior sealing performance and extended service life due to their simple design and favorable casting characteristics.
- Application Range: These valves are versatile, suitable for interrupting or diverting fluid flow in pipelines carrying various media such as water, steam, oil, nitric acid, acetic acid, oxidizing agents, urea, and more. They are extensively utilized, particularly in petroleum pipelines.
- Maintenance Considerations: Preventing water ingress into the electric head and transmission mechanisms during maintenance is crucial for preventing rusting or freezing of components. Regular maintenance ensures prolonged service life and reliable operation of forged steel gate valves.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Forged steel gate valves have several advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of valves. Here's a breakdown:
The Major Advantages
- Reduced fluid resistance: Forged steel gate valves offer minimal resistance to fluid flow in pipelines, facilitating smooth flow.
- Low force requirement for operation: The use of forged materials makes the operation of forged steel gate valves relatively lightweight.
- Unrestricted fluid flow direction: The design of forged steel gate valves allows fluid flow in any direction, providing substantial flow capacity.
- Reduced erosion of sealing surfaces: When fully open, forged steel gate valves experience less erosion of sealing surfaces from working fluids compared to globe valves, thus enhancing sealing performance and service life.
- Simple design and favorable casting characteristics: The straightforward design and good casting characteristics of forged steel gate valves simplify production and maintenance processes.
Several Disadvantages
- Large physical dimensions: The physical dimensions of forged steel gate valves are relatively large, requiring ample installation space.
- Potential for relative friction during operation: Due to the large contact area between the valve disc and seat, forged steel gate valves may experience relative friction during operation, which could affect their service life.
- Complexity in machining, grinding, and maintenance: Forged steel gate valves typically feature two sealing surfaces, resulting in complex machining, grinding, and maintenance processes, increasing maintenance difficulty.
Application Range
Forged steel gate valves are suitable for Class 150 to 2500 pipelines, operating at temperatures ranging from -29 to 425°C (carbon steel) or -29 to 500°C (stainless steel). They are employed for interrupting or diverting fluid flow in pipelines, finding widespread application in sectors like petroleum pipelines.
In summary, forged steel gate valves are integral components in industrial fluid control systems, renowned for their exceptional performance and reliability. With ongoing technological advancements, forged steel gate valves are poised to play an increasingly vital role in providing stable and dependable fluid control solutions for industrial applications.

